

Plants need nutrients when they start to grow after the dormant phase. The frequency and timing of fertilization depends on the specific needs of the plant and the type of fertilizer used. Some plants require frequent fertilization, while others only need to be fertilized once or twice a year.
To determine whether your plant needs fertilizer, we observe changes in the salt content, light, moisture absorption and temperature and analyze the growth rate with a view to the species-specific needs of the plant. From this, we derive the nutrient requirements and recommend a date in the future when you should fertilize or repot.

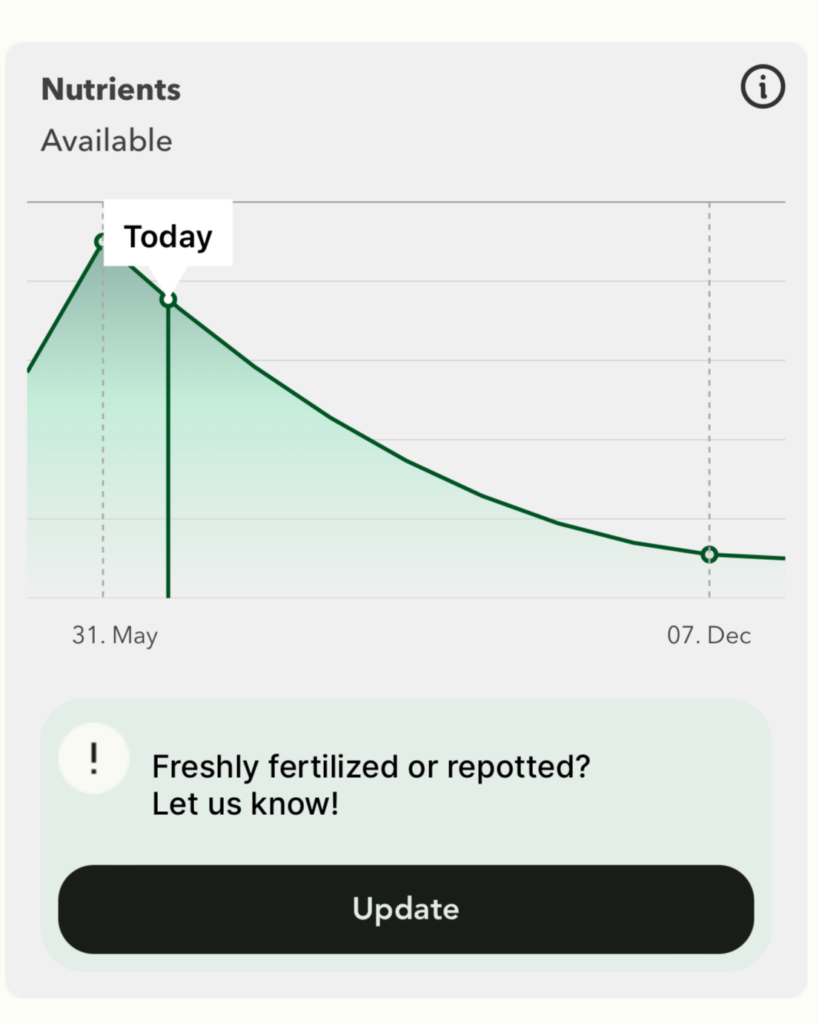
The curve you see in the app does not really show measurements, as you know it from the moisture curve, for example. It merely shows that the nutrient content in the substrate will fall until the day of the next fertilization and shows you:
1. the date on which the plant was last fertilized or repotted (here: 31 May)
2. how far away you are from the next recommended fertilization or repotting date (here: today)
3. when you should fertilize or repot the next time (here: 07 Dec)
In addition, we take into account information that you give us about the last fertilization or the last addition of fresh, nutrient-rich soil. Although we can analyze the needs of your plant over time, we cannot reliably determine the existing nutrient content at the beginning, as this, or the availability of nutrients, depends not only on the salt content, but also on variables such as the pH value. Your input will help us to improve the analysis. The fertilization recommendation is not static, but adapts dynamically depending on environmental conditions, season, user input, etc.
If the FYTA Beam detects that your plant is in the dormant phase (usually in winter) due to changes in environmental factors, the fertilization recommendation in the graph is shifted further into the future, as your plant can now manage without, or with a small amount of nutrients. If the season changes from the dormant phase to the growth phase, you are recommended to fertilize more frequently again.
We include salinity measurements in our long-term nutrient analysis, but not as a stand-alone variable. However, you can display the salinity measurements in live mode to test soil samples. Make sure that the soil samples are thoroughly saturated with water before you test them. Salinity is measured in electrical conductivity and expressed as microsiemens per centimeter (mS/cm), where 1 mS = 1000 µS.

